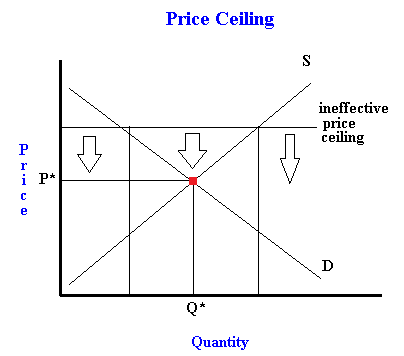
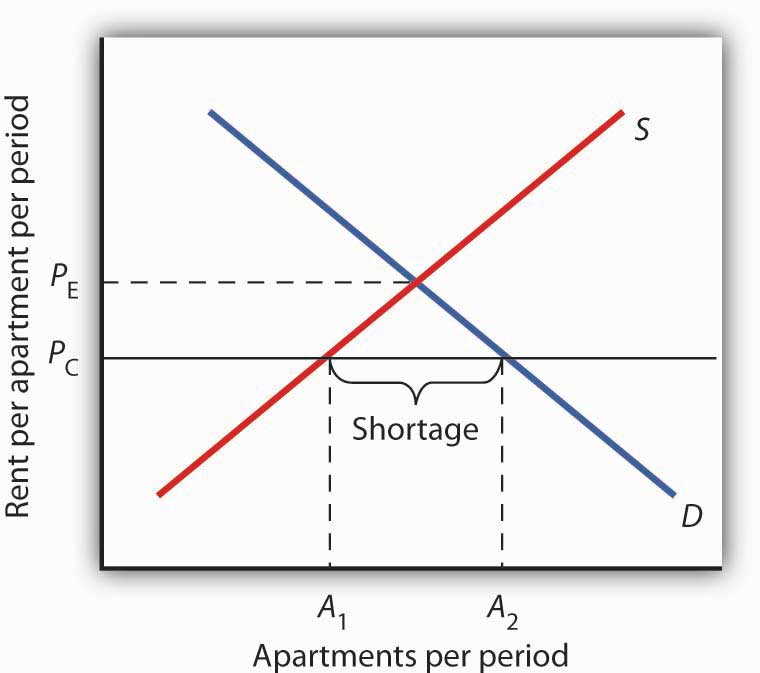
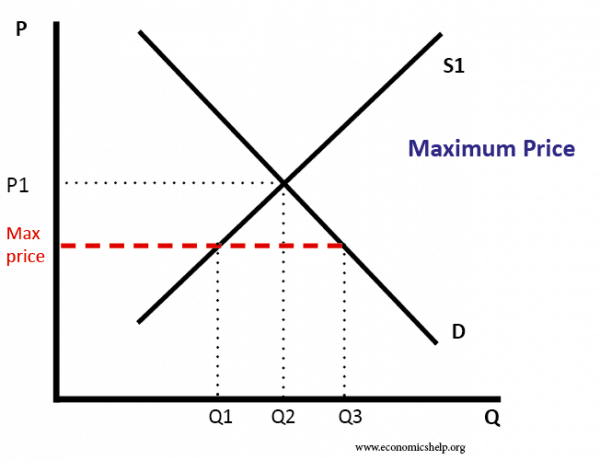
In pharmacology a ceiling effect is the point at which an independent variable which is the variable being manipulated is no longer affecting the dependent variable which is the variable being measured.
Define floor ceiling effects.
Let s talk about floor and ceiling effects for a minute.
The term ceiling effect has two distinct meanings referring to the level at which an independent variable no longer has an effect on a dependent variable or to the level above which variance in an independent variable is no longer measured or estimated.
This is even more of a problem with multiple choice tests.
The floor effect is a test measure that won t go below a certain point.
In layperson terms your questions are too hard for the group you are testing.
It essentially describes when the dependent variable has leveled out and is no longer responding to the independent variable.
In statistics a floor effect also known as a basement effect arises when a data gathering instrument has a lower limit to the data values it can reliably specify.
The inability of a test to measure or discriminate below a certain point usually because its items are too difficult.
The other scale attenuation effect is the ceiling effect.
The other scale attenuation effect is the floor effect the ceiling effect is observed when an independent variable no longer has an effect on a dependent variable or the level above which variance in an independent variable is no longer measurable.
An example of use in the first area a ceiling effect.
Ceiling effect is used to describe a situation that occurs in both pharmacological and statistical research.
There is very little variance because the floor of your test is too high.
The ceiling effect is one type of scale attenuation effect.