The federal minimum wage at the.
Disequilibrium price floor.
Perhaps the best known example of a price floor is the minimum wage which is based on the normative view that someone working full time ought to be able to afford a basic standard of living.
Ineffective price ceilings tend to be too low.
In either case the price must change to achieve an equilibrium price that balances supply and demand.
Ineffective price floors tend to be too high.
A good example of how price floors can harm the very people who are supposed to be helped by undermining economic cooperation is the minimum wage.
Like price ceiling price floor is also a measure of price control imposed by the government.
Unfortunately it like any price floor creates a surplus.
Binding floor price gives chance to the government to set prices on certain goods that are high and it also creates economic disequilibrium.
Check all that apply.
Price floor is a situation when the price charged is more than or less than the equilibrium price determined by market forces of demand and supply.
If supply greatly exceeds demand then the price is set too high.
Legislating a minimum wage is commonly seen as an effective way of giving raises to low wage workers.
A price floor is the lowest legal price that can be paid in markets for goods and services labor or financial capital.
It is legal minimum price set by the government on particular goods and services in order to prevent producers from being paid very less price.
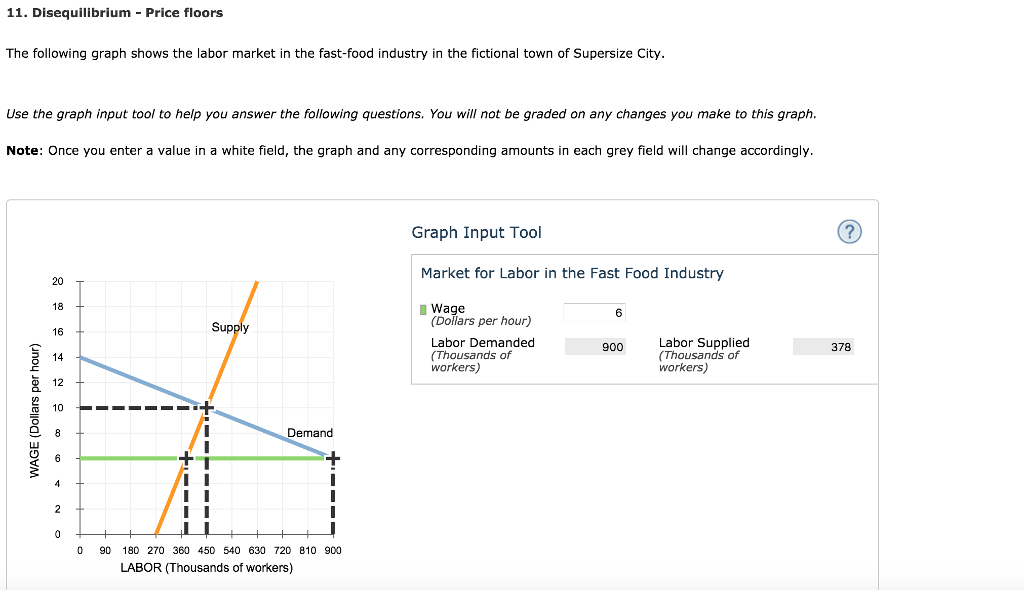
If the government imposes a price floor on wheat at 5 predict the amount of disequilibrium.
Service tax is a tax levied by the government on service providers on certain service transactions but is actually borne by the customers.
A possible result of disequilibrium is excess demand lower demand.
But this is a control or limit on how low a price can be charged for any commodity.
There will be a surplus of 3 000 000 if the government imposes a price floor on wheat at 5 and agrees to purchase any surpluses how much will the government be forced to spend.
Which statements correctly explain price floors and price ceilings.
In a free market you would expect firms to deal with this disequilibrium by putting up the price to ration the demand.
With a price of p1 the demand q1 is greater than the supply q3.
This can be a short term byproduct of.
In this case it is a surplus of.
This disequilibrium will lead to a shortage q1 q3 and long queues as consumers try to get the limited supply.
A possible result of disequilibrium is.
Disequilibrium is a situation where internal and or external forces prevent market equilibrium from being reached or cause the market to fall out of balance.
Disequilibrium due to price below equilibrium.